Your carbon report – clear insight into your emissions

Your carbon report – clear insight into your emissions
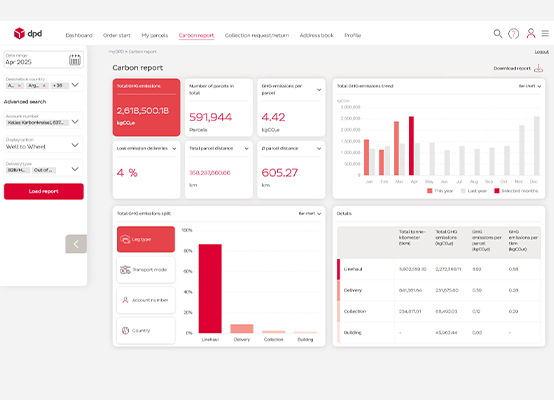
The DPD carbon report provides you with a transparent overview of the emissions generated by your parcel shipments. The report for commercial shipments is available in real time for past and completed months at any time in the myDPD business customer portal and can be conveniently downloaded.
Certified and reliable
Based on approved standards such as GLEC Framework, ISO 14083 and EN 17837 for maximum credibility and reliability.
Simple and comprehensive
The carbon report makes complex emissions calculations easily accessible and presents them in an comprehensible manner.
Sustainability report
As a business customer, DPD supports you in providing individual data and automated reports for your sustainability reporting.
How do we calculate the carbon report?
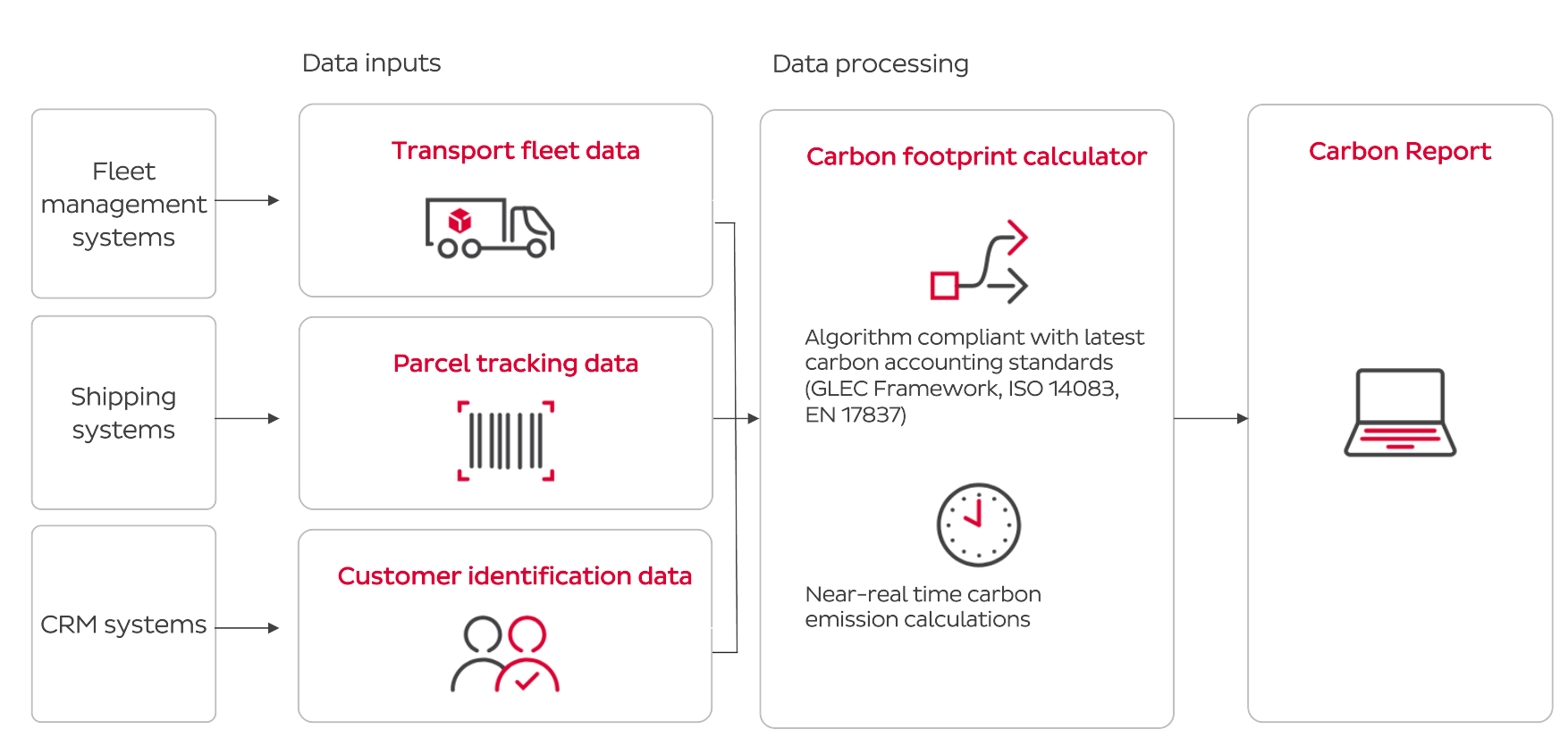
The carbon dashboard easily explained
-
Carbon dashboard
The interactive dashboard displays key figures such as total emissions and emissions per parcel, as well as individual evaluations. Filters and diagrams can be used to identify trends and analyse details. -
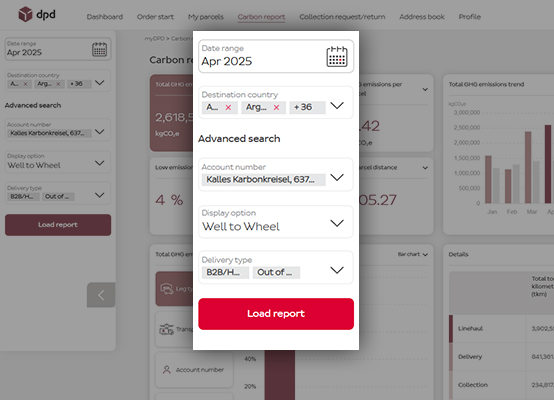
Filter options
By using filters, you can sort by date, country, pick-up location, vehicle life cycle or delivery type and analyse specific data. -
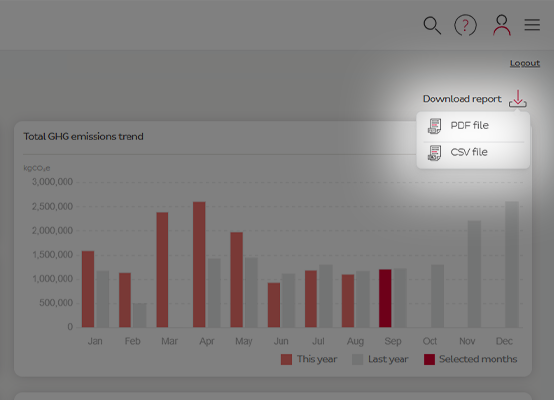
Download carbon report
The carbon report can be downloaded at any time in PDF or CSV format and contains all the relevant information for your sustainability reporting. -
GHG emissions
The calculated GHG emissions can be categorised according to various criteria. In addition, the temporal course of the emission generation can be visualised in order to track its development.
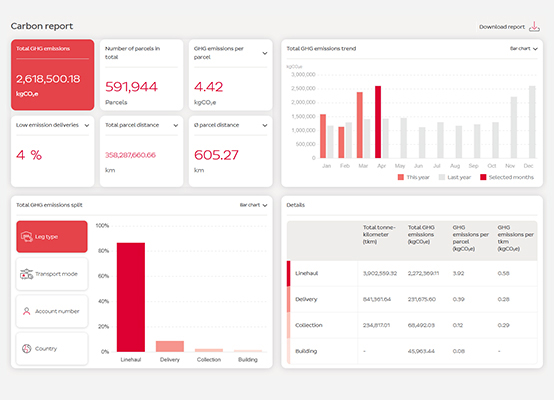
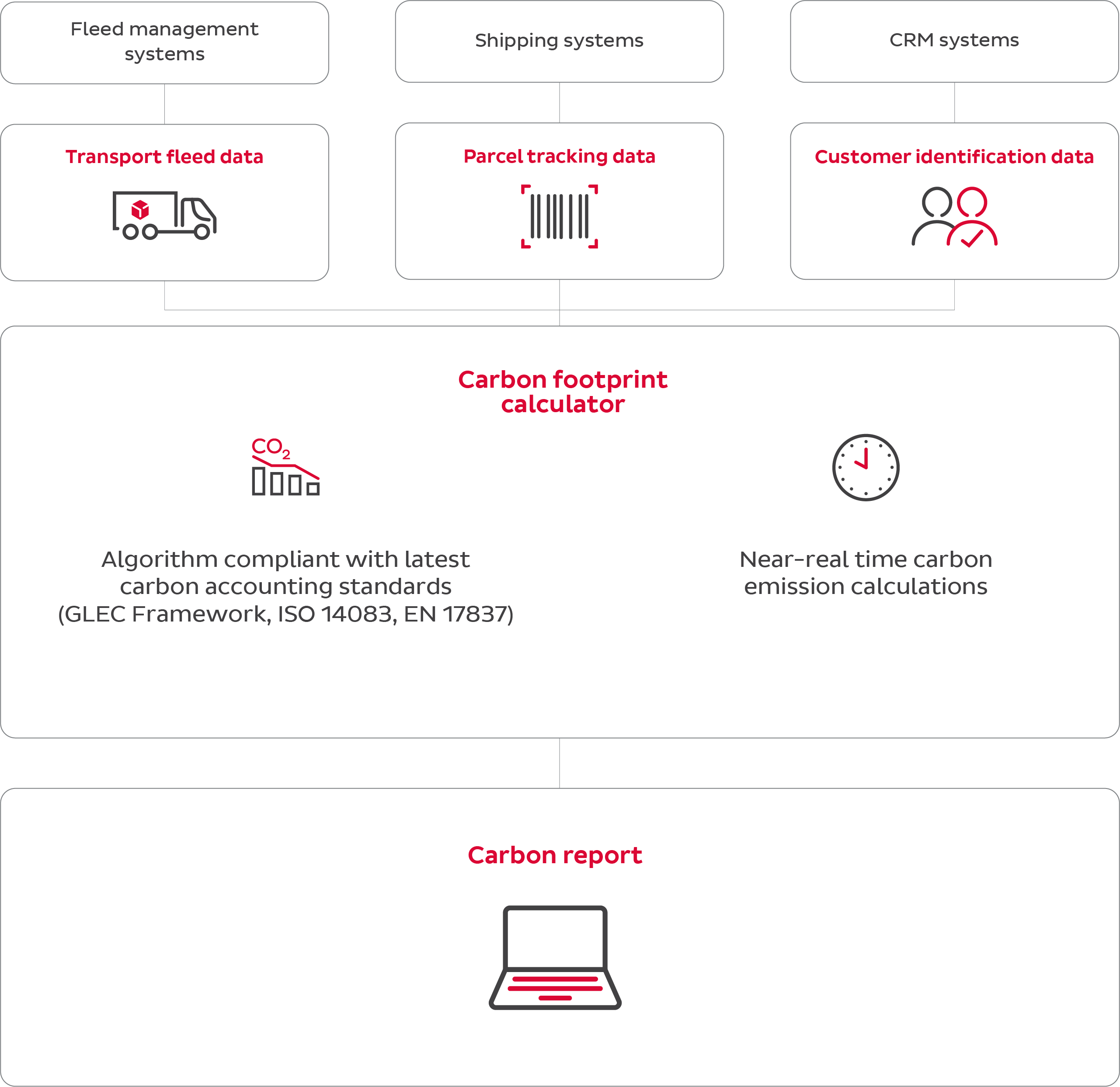
Carbon dashboard
The interactive dashboard displays key figures such as total emissions and emissions per parcel, as well as individual evaluations. Filters and diagrams can be used to identify trends and analyse details.

Filter options
By using filters, you can sort by date, country, pick-up location, vehicle life cycle or delivery type and analyse specific data.

Download carbon report
The carbon report can be downloaded at any time in PDF or CSV format and contains all the relevant information for your sustainability reporting.

GHG emissions
The calculated GHG emissions can be categorised according to various criteria. In addition, the temporal course of the emission generation can be visualised in order to track its development.

Questions and answers about the carbon report

 Where can I find the carbon report?
Where can I find the carbon report?
You can find the carbon report directly in your myDPD for business customers account. It is integrated into the menu there and can be accessed at any time.

 What standards is DPD's carbon report based on?
What standards is DPD's carbon report based on?
The carbon report is based on internationally approved standards to make sure emissions are calculated in a reliable and clear way. These include:
- ISO 14083: This standard sets out a consistent way to measure and report greenhouse gas emissions from passenger and freight transport.
- EN 17837 (PDEF – Parcel Delivery Environmental Footprint): This standard defines the calculation and declaration of greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants specifically for parcel logistics services.
- GLEC Framework: A globally approved framework for emissions reporting in logistics, developed by the Global Logistics Emissions Council (GLEC).

 Why does my carbon report not contain any data?
Why does my carbon report not contain any data?
If your carbon report does not show any results, this usually means that either no data is available for the period or an error has occurred during data collection. In this case, you should:
- Check the data source: Make sure that all shipping data has been transmitted correctly.
- Check error messages: Check whether technical errors have prevented data collection.
- Contact support: If the problem persists, our support team ([email protected]) is available to identify and fix the error.

 What do the technical terms in the carbon report mean?
What do the technical terms in the carbon report mean?
Term | Definition |
GHG | Greenhouse Gases: The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect, linked to human activities, are carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), nitrous oxide (N₂O) and the fluorinated gases (HFC, PFC, SF₆ und NF₃). |
CO₂e | Human activity emits different kind of GHG. Their Global Warming Potential (GWP), a physical characteristic of a GHG, represents their impact on the greenhouse effect, and allows to convert 1 kg of GHG into X kg of CO₂ equivalent, noted CO₂e. It allows emissions of different gases to be compared. Thus, CO₂e is the same as GHG in that it covers all greenhouse emissions as opposed to CO₂ which only refers to carbon dioxide. |
Scope 1, 2, 3 | Scope 1 emissions are direct GHG emissions from company-owned and controlled resources. Scope 2 emissions are indirect GHG emissions from the generation of purchased energy. Scope 3 emissions are all indirect GHG emissions – not included in scope 2 – that occur in the value chain. |
Emission factor | Coefficient which allows to convert activity data (vehicle fuel consumption, kWh of a given energy, etc.) into Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It is the average emission rate of a given source, relative to units of activity or process/processes. |
LEG | Transportation connection between two points. Leg types can be linehaul, air, sea, rail, pick up or delivery. |
Ton.Km | Unit of measurement corresponding to the transport of one ton over one kilometer (e.g. Transporting 3 tons of goods over a distance of 150 kilometers corresponds to a transport activity of 3 x 150 = 450 t.km). |
Parcel.km | Unit of measurement corresponding to the transport of one parcel over one kilometer (e.g. Transporting 1000 parcels over a distance of 150 kilometers corresponds to a transport activity of 1000 x 150 = 150 000 parcel.km). |
Well-to-Wheel (WTW) | GHG emissions are calculated over the entire value chain: Well-to-tank (WTT): Fuel production and distribution. |
Smart Freight Centre | International non-profit organization focused on reducing greenhouse gas emission from freight transportation. |
GLEC Framework | The global methodology for harmonised calculation and reporting of the logistics GHG footprint across the multi-modal supply chain. It can be implemented by shippers, carriers and logistics service providers. It is aligned to the GHG Protocol. |
ISO 14083 | ISO 14083 establishes a common methodology for the quantification and reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions arising from the operation of transport chains of passengers and freight. |
EN 17837 | Methodology for calculation and declaration of GHG emissions and Air pollutants of parcel logistics delivery services, it provides the principles and rules for the quantification, allocation and reporting of environmental impacts from parcel logistics delivery services. Also called Parcel Delivery Environmental Footprint (PDEF). |
GHG Protocol | GHG Protocol establishes comprehensive global standardised frameworks to measure and manage GHG emissions from private and public sector operations, value chains and mitigation actions. |
Term
GHG
Term
CO₂e
Term
Scope 1, 2, 3
Term
Term
LEG
Term
Ton.Km
Term
Parcel.km
Term
Well-to-Wheel (WTW)
Term
Smart Freight Centre
Term
GLEC Framework
Term
ISO 14083
Term
EN 17837
Term
GHG Protocol
Definition | Greenhouse Gases: The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect, linked to human activities, are carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), nitrous oxide (N₂O) and the fluorinated gases (HFC, PFC, SF₆ und NF₃). | Human activity emits different kind of GHG. Their Global Warming Potential (GWP), a physical characteristic of a GHG, represents their impact on the greenhouse effect, and allows to convert 1 kg of GHG into X kg of CO₂ equivalent, noted CO₂e. It allows emissions of different gases to be compared. Thus, CO₂e is the same as GHG in that it covers all greenhouse emissions as opposed to CO₂ which only refers to carbon dioxide. | Scope 1 emissions are direct GHG emissions from company-owned and controlled resources. Scope 2 emissions are indirect GHG emissions from the generation of purchased energy. Scope 3 emissions are all indirect GHG emissions – not included in scope 2 – that occur in the value chain. | Coefficient which allows to convert activity data (vehicle fuel consumption, kWh of a given energy, etc.) into Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It is the average emission rate of a given source, relative to units of activity or process/processes. | Transportation connection between two points. Leg types can be linehaul, air, sea, rail, pick up or delivery. | Unit of measurement corresponding to the transport of one ton over one kilometer (e.g. Transporting 3 tons of goods over a distance of 150 kilometers corresponds to a transport activity of 3 x 150 = 450 t.km). | Unit of measurement corresponding to the transport of one parcel over one kilometer (e.g. Transporting 1000 parcels over a distance of 150 kilometers corresponds to a transport activity of 1000 x 150 = 150 000 parcel.km). | GHG emissions are calculated over the entire value chain: Well-to-tank (WTT): Fuel production and distribution. | International non-profit organization focused on reducing greenhouse gas emission from freight transportation. | The global methodology for harmonised calculation and reporting of the logistics GHG footprint across the multi-modal supply chain. It can be implemented by shippers, carriers and logistics service providers. It is aligned to the GHG Protocol. | ISO 14083 establishes a common methodology for the quantification and reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions arising from the operation of transport chains of passengers and freight. | Methodology for calculation and declaration of GHG emissions and Air pollutants of parcel logistics delivery services, it provides the principles and rules for the quantification, allocation and reporting of environmental impacts from parcel logistics delivery services. Also called Parcel Delivery Environmental Footprint (PDEF). | GHG Protocol establishes comprehensive global standardised frameworks to measure and manage GHG emissions from private and public sector operations, value chains and mitigation actions. |

 Can I integrate the carbon report via API?
Can I integrate the carbon report via API?
Yes, the carbon report can be integrated via API. Further information can be found here.
You can find helpful information here.
Home / Support / myDPD help and useful information / CO2-Report